Introduction
Acute musculoskeletal pain is a prevalent condition impacting millions of individuals worldwide. This type of pain arises suddenly and is usually associated with injury, overuse, or specific musculoskeletal disorders. Effective management of acute musculoskeletal pain is critical to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Pain O Soma 500 mg, containing the active ingredient carisoprodol, is a widely used medication in the treatment of such pain. This essay delves into the science behind Pain O Soma 500 mg, comparing it with Pain O Soma 350 mg, and explores the mechanisms, efficacy, and safety of these treatments in managing acute musculoskeletal pain.
Understanding Acute Musculoskeletal Pain
Definition and Pathophysiology
Acute musculoskeletal pain is defined as pain that originates from the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, or soft tissues and lasts for a short duration, typically less than three months. The pathophysiology of acute musculoskeletal pain involves the activation of nociceptors (pain receptors) due to tissue injury or inflammation. This activation leads to the transmission of pain signals through the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system, where the pain is perceived.
Common Causes
- Trauma or Injury: Such as fractures, sprains, and strains, often resulting from accidents or falls.
- Overuse or Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive motion or overexertion can lead to conditions like tendinitis or bursitis.
- Muscle Spasms: Sudden, involuntary contractions of muscles that can cause significant pain and discomfort.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or gout that cause inflammation in the musculoskeletal system.
- Infections: Osteomyelitis and other infections that affect the bones or muscles.
Pain O Soma: An Overview
Composition and Formulation
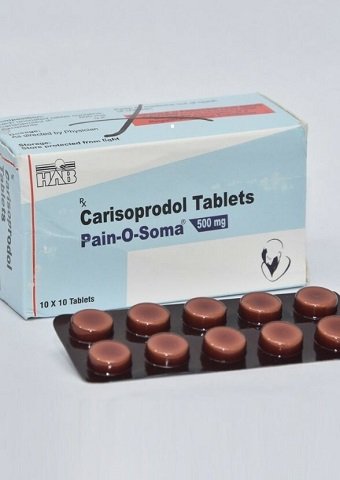
Pain O Soma 500 mg Tablet is available in two common dosages: 350 mg and 500 mg. Both formulations contain carisoprodol as the active ingredient, a centrally acting muscle relaxant. Carisoprodol is metabolized in the liver to form meprobamate, which has anxiolytic and sedative properties.
Mechanism of Action
Carisoprodol works by interrupting neuronal communication within the reticular formation and spinal cord, resulting in sedation and alteration of pain perception. The exact mechanism by which carisoprodol alleviates muscle pain is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve:
- GABAergic Effects: Carisoprodol and its metabolite meprobamate may enhance the inhibitory effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, leading to muscle relaxation and pain relief.
- Inhibition of Interneuronal Activity: By reducing interneuronal communication, carisoprodol decreases the reflexive muscle contractions that contribute to pain.
Clinical Use of Pain O Soma
Indications
Pain O Soma is primarily indicated for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. It is often prescribed for:
- Muscle spasms
- Lower back pain
- Acute strains and sprains
Dosage and Administration
- Pain O Soma 350 mg: Typically, the dosage is one tablet taken three times a day and at bedtime.
- Pain O Soma 500 mg: Prescribed similarly, with the dose adjusted based on the severity of the condition and patient response.
It is important to adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration to avoid dependency and potential side effects. Treatment duration is usually short-term, not exceeding two to three weeks.
Efficacy of Pain O Soma
Comparative Studies
Clinical studies have compared the efficacy of Pain O Soma 350 mg and 500 mg in managing acute musculoskeletal pain. Research indicates that:
- Pain Relief: Both dosages are effective in reducing pain, with the 500 mg dosage providing more pronounced relief in patients with severe pain.
- Onset of Action: Pain relief typically begins within 30 minutes to an hour after oral administration, with peak effects occurring within two hours.
- Duration of Effect: The analgesic effects of carisoprodol last for approximately 4-6 hours, necessitating multiple doses throughout the day.
Patient Outcomes
Patients taking Pain O Soma report significant improvements in pain levels, muscle relaxation, and overall functionality. The higher dose (500 mg) is often reserved for cases where lower doses (350 mg) do not provide sufficient relief.
Safety and Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Both dosages of Pain O Soma can cause side effects, although the incidence and severity may vary. Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Serious Side Effects
More severe side effects, which require immediate medical attention, can include:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat)
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Seizures
- Loss of coordination
Dependency and Abuse Potential
Carisoprodol has the potential for abuse and dependency, particularly with prolonged use or higher doses. It is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in many countries. Signs of dependency include:
- Craving for the medication
- Increased tolerance (requiring higher doses for the same effect)
- Withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation
Contraindications and Precautions
Patients should inform their healthcare provider of their complete medical history, especially if they have:
- A history of substance abuse
- Liver or kidney disease
- Seizure disorders
- Allergies to carisoprodol or related compounds
It is also advisable to avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants while taking Pain O Soma, as they can enhance the sedative effects and increase the risk of side effects.
Alternative Treatments for Acute Musculoskeletal Pain
While Pain O Soma is effective, it is not suitable for everyone. Alternative treatments include:
Non-Pharmacological Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Massage Therapy: To relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
- Acupuncture: Traditional Chinese medicine technique to relieve pain.
Pharmacological Alternatives
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Acetaminophen: An analgesic for pain relief without anti-inflammatory effects.
- Opioids: For severe pain, but with a high risk of addiction and side effects.
- Muscle Relaxants: Other muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine or methocarbamol.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind Pain O Soma 500 mg and its use in treating acute musculoskeletal pain is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. Carisoprodol’s effectiveness in relieving pain and muscle spasms makes it a valuable treatment option, particularly for short-term use. However, the potential for side effects and dependency n ecessitates careful prescribing and monitoring. By comparing Pain O Soma 350 mg and 500 mg, clinicians can tailor treatment to the individual needs of patients, ensuring optimal pain management and improved quality of life. As with any medication, the benefits must be weighed against the risks, and alternative treatments should be considered based on patient-specific factors.
RELATED POSTS
View all